Process mapping is a powerful tool for improving processes and systems and managing projects, explains Ayanna Castro
Imagine this. You are named the project lead for a major project. You’ve been tasked with creating a new employee onboarding process that incorporates input from multiple departments. The goal of this new process is to assist new employees to acclimate to their respective departments as well as the entire organization. You gather information from several departments and submit a standard operating procedures document. After review, it’s determined that while the document is thorough, it provides too much of the “why” without providing enough information on the “how.” This is the perfect time to utilize process mapping.
What Is a Process Map?
Similar to mind mapping and also known as a flowchart, process model, or workflow diagram, process mapping shows who and what is involved in a process. It shows areas where a process should and can be improved. It also helps to identify input and resources needed to effectively and efficiently complete projects. Process maps can be as simple as a single piece of paper or as complex as an entire wall. The degree of detail needed depends on the purpose, audience, and complexity of the process.
Benefits and Purpose of Process Mapping
The biggest benefit of process mapping is uncovering waste in resources (time, people, or budget). The overall purpose of process mapping is to improve the performance and efficiency of a process or system, as well as increase the quality of the output, and increase customer and stakeholder satisfaction.
Process mapping is used to:
- Identify wastefulness and blockages by identifying areas where the process is slow and prone to errors.
- Streamline and enhance the process by providing structure for identifying problems and implementing process improvements, such as eliminating unnecessary steps, reducing delays, and automating repetitive tasks.
- Standardize the process to provide a clear and consistent approach to performing the process, which helps to ensure that all stakeholders understand and follow the same procedures and guidelines.
- Improve communication and collaboration to clarify the roles and responsibilities of different stakeholders, and to identify potential areas of conflict or misunderstanding by visualizing the expected workflow.
Steps to Create a Process Map
With the development of software, process mapping has become streamlined. However, process maps can also be created in Microsoft Word, PowerPoint or Excel.
Step 1: Identify the problem
What is the process that needs be visualized or the problem to be solved?
Step 2: Brainstorm activities involved
This is where you list the steps of the process and decide what level of detail to include. Each step should include who does it and when it is done. To ensure a comprehensive list of steps, assemble a team of stakeholders who are impacted by the process.
Step 3: Identify boundaries
Where or when does the process start and stop?
Step 4: Determine and sequence steps
Who is responsible for each task? What is the timeline to complete each task?
Step 5: Draw the flowchart
Each element of a process map is represented by a flowchart symbol:
Oval: beginning or stopping of a process
Rectangle: operation or activity that needs to be done
Arrow: flow of direction
Diamond: point of decision; arrows coming out of the diamond are usually labeled yes or no
Parallelogram: input or output
Step 6: Finalize the process map
At this point, share the process map with stakeholders (team members, managers, customers, etc.) for agreement. During the review process, ask if the process is running as it should be, if anything is redundant, if there are any steps missing and most importantly, if everyone is in agreement with the process.
Types of Process Maps
Overall, the type of process map used depends on the specific goals and requirements of the project. It also depends on the level of detail and complexity needed to understand and improve the process. There are several types of process maps and the most popular are high-level, detailed and swimlane (cross-functional).
Flowchart
The simplest form of a process map is a basic flowchart. The basic flowchart uses process mapping symbols to illustrate the inputs and outputs of a process and the steps included in completing the process. Basic flowcharts can be used to plan new projects, improve communication between team members, model and document processes, solve problems in a current process, and analyze and manage workflows. This type of map is best for showing how a process is done from start to finish, typically in sequential order.
High-level process map
This map provides quick and easy insights into what the process does without getting into the detail of how it’s done. It is helpful when communicating to leadership and others who have little to no interest in the details. This map shows where all the inputs go and where all the outputs are created.
Detailed process map
This map is typically used when you do not need to see the entire process in detail, but there might be some parts of the process that require additional detail. To start, consider the input for the step, then identify what immediately happens with that input and repeatedly ask “What happens next?” until the output is produced.
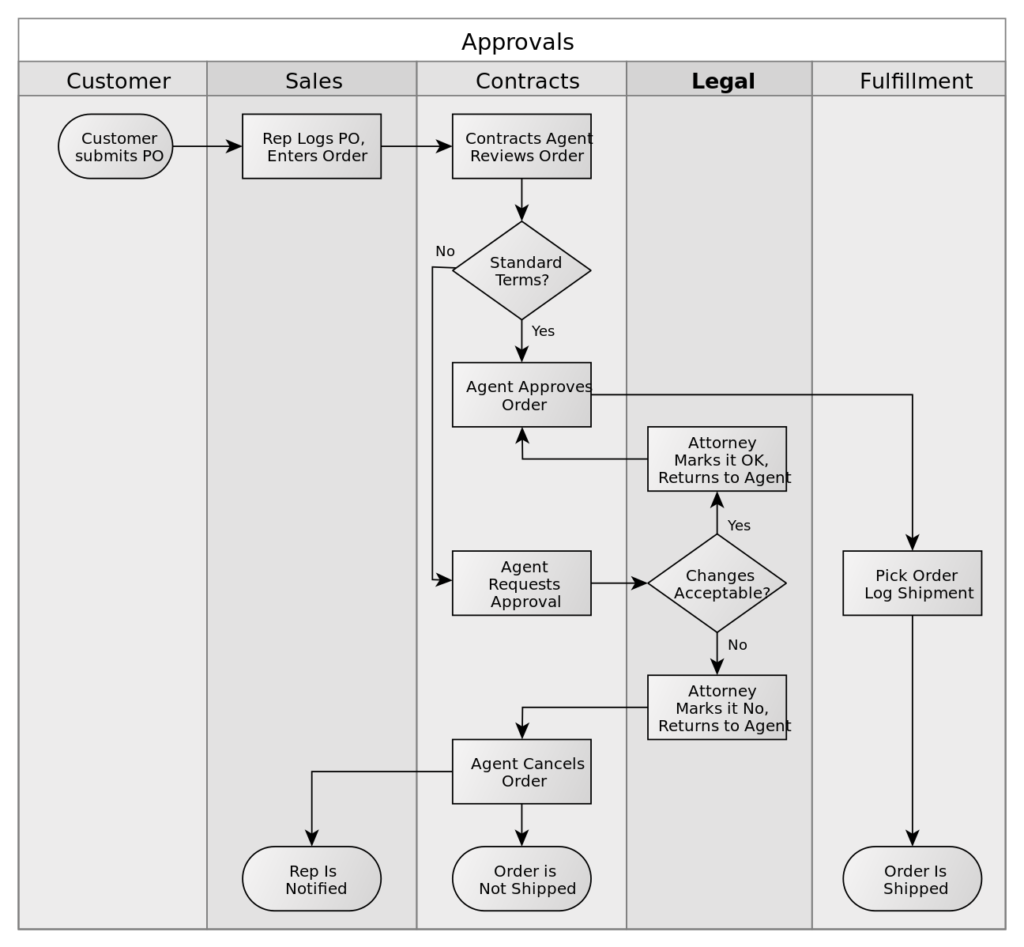
Swimlane (cross-functional) map
A swimlane diagram shows the steps in a process as they relate to different departments, roles, or individuals. Swimlane diagrams help to identify the key roles taking part in a process and their relation to each other. In addition, they show how a process operates throughout the business and determine failures and redundancies. The swimlane map is helpful when establishing work instructions or training for a new process.
Benefits of Process Mapping
Increased efficiency
Process mapping helps identify inadequacies in a process and reveals opportunities for improvement, such as reducing bottlenecks, eliminating unnecessary steps, and automating repetitive tasks. By streamlining the process, organizations can save time and resources and increase productivity.
Enhanced communication
Process mapping provides a common language and framework for discussing and understanding the process among different stakeholders. This enhances communication, collaboration, and decision-making, and reduces misunderstandings.
Improved transparency
Process mapping provides a clear and transparent view of the process, including its inputs, outputs, and dependencies, as well as the roles and responsibilities of different stakeholders. This enhances accountability and helps to identify areas for improvement and optimization.
Improved training and development
Process mapping provides a clear and structured framework for training new employees and developing their skills and knowledge. By standardizing the process and providing clear instructions and feedback, organizations can improve the quality and consistency of their workforce.
Process Mapping and Project Management
Process mapping can be a useful tool for managing projects because it helps to visualize the project workflow and areas for improvement. Here are some steps to use process mapping to manage projects:
Identify the project scope and objectives
Before starting the process mapping, it’s important to define the project scope and objectives, including the deliverables, timelines, and budget.
Identify the key processes
Identify the key processes and tasks involved in the project, including the inputs, outputs, and dependencies.
Map the processes
Use a flowchart or other visualization tool to map out the project processes and tasks, including the sequence of steps, decision points, and feedback loops.
Analyze the process flow
Analyze the process flow to identify potential delays and look for opportunities to streamline the workflow or reduce the time and effort required for each step.
Implement and monitor the process improvements
Implement the process improvements and monitor their impact on the project performance, such as the time, cost, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Pro Tips for Process Mapping
Define the scope of the process
Before starting the process mapping exercise, it’s important to define the boundaries and scope of the process to be mapped. This will help to ensure the map accurately reflects the process and its key components.
Involve all stakeholders
It’s important to involve all stakeholders who are part of or affected by the process in the mapping exercise. This includes team members, customers, suppliers, and other relevant parties. This will help to ensure that the map reflects all aspects of the process and incorporates different perspectives.
Continuously improve the process
Once the process map has been created, use it to identify opportunities for improvement and to implement changes to the process. This will help to continuously optimize the process and ensure that it remains efficient and effective over time.
Conclusion
Overall, process mapping is a powerful tool for improving processes and systems. By using process mapping to manage projects, you can improve project efficiency, reduce the risk of errors or delays, and ensure that the project meets the stakeholders’ requirements and expectations.
Sources
Lucidchart, GoLean, Six Sigma, Indeed, Asana, Project Management Institute












kindly help me identify process mapping of the administrative assistant in receiving information.