Take your seat and navigate your journey to mastering AI skills and making it your superpower, says Julia Schmidt
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming a hot topic for many. Our organizations are rapidly integrating AI technologies into various workflows. As Executive Support professionals, we are expected to use generative AI (GenAI) tools to enhance our work’s efficiency and agility. Research indicates that our profession is at the forefront of making AI a practical reality in the workplace. According to recent studies, the use of generative AI has nearly doubled in the last six months, with 75% of global knowledge workers now utilizing it.
This article delves into how we can leverage these tools to maximize our productivity by optimizing prompt engineering. Executive Support professionals are witnessing firsthand how AI reshapes our roles and responsibilities. A recent report from Microsoft and LinkedIn highlights that employees are eager for AI adoption and are unwilling to wait for companies to catch up.
To stay ahead, I have been exploring the art of prompt engineering. I have tested many techniques to interact with GenAI tools, such as ChatGPT and CoPilot. I wanted to improve how I ask for help and optimize the output I get from these tools. Also, I wanted to polish my AI skills to maintain a competitive edge in the workforce, as AI trends show that artificial intelligence is not a technical skill reserved solely for those in technical occupations. I am going to explain the meaning of prompt engineering, share a prompting technique, and show how I have applied it. Finally, I will recommend some actions for you to make prompt engineering your superpower. I am currently undertaking training in prompt engineering.
Prompt Engineering
A prompt is simply a question or instruction you give to the tool, while prompt engineering is the art of crafting these questions or instructions in a way that makes the AI give you the best possible answer. Prompt engineering patterns are common methods or templates used to structure these questions or instructions. They help ensure the AI understands exactly what you want. It’s like following a cooking recipe to ensure your dish turns out great.
Prompt engineering is the process of writing, refining, and optimizinginputs to encourage generative AI systems to create specific, high-quality outputs.
The goal is to communicate with the GenAI tools as if you’re instructing a very literal-minded assistant. The more precise and detailed your instructions, the better the AI can perform the task.
Think of ChatGPT and CoPilot as your AI assistant. They are here to help you deliver on your tasks. For the ultimate result, you need to learn how to communicate with your assistant. Are you familiar with that?
I have also asked ChatGPT the meaning of prompt engineering, and here is the answer:

Three Ways to Embrace GenAI Tools
Think of GenAI tools as your AI assistant, collaborator, and advisor. They are here to help you deliver on your tasks:
Assistant
GenAI tools can handle routine tasks, draft communications, and manage schedules, like a Personal or Executive Assistant.
Collaborator
These tools can work alongside you to brainstorm ideas, provide feedback, and support creative processes, acting as a collaborative team member.
Advisor
GenAI can analyze data, provide insights, and suggest strategies, much like a consultant or advisor offering expert guidance.
The better you understand and communicate with these AI tools, the more effectively they can assist you in achieving your goals.
Prompt Engineering Techniques
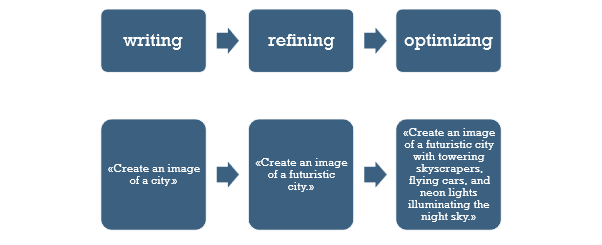
In the example below, we have the three main steps of a prompting technique from simply writing a request to optimizing it to receive the right output.

In addition to that, I want you to be aware of five general recommendations to help improve your prompting skills. They are related to being clear and specific, providing context, giving examples of desired output, adjusting your prompts, and setting parameters. Here is what ChatGPT recommends for you to become better at prompting:

The Prompt Elements
There are four elements you need to know about prompt engineering and how to optimize your interaction with GenAI tools. These elements are overall the same in all techniques I have explored. The terminology may change, but the concept remains the same. It’s all about specifying the instruction you give to the tool, defining the context of the situation, and asking the right questions to get the best result.
Instruction: a specific task or instruction you want the model to perform
Context: external information or additional context that can steer the model to better responses
Input Data: the input or question for which we are interested in finding a response
Output Indicator: the type or format of the output
Be specific about the instruction and task you want the model to perform. The more descriptive and detailed the prompt is, the better the results. Consider how specific and detailed you should be in giving the context. The details should be relevant and contribute to the task at hand. Experimentation and creativity are essential to optimize the prompts when interacting with the tool.
For the context, use the “act as” technique. This technique helps the tool understand which persona it must act as (follow) and establishes the context for the upcoming instruction or question.
For the input data, formulate the question expressing the problem you want the tool to solve.
And finally, for the output indicator, give the tool as much information as possible to help it understand how to perform the task best.
Let’s see an illustration of the four elements with a complete prompt related to getting output to create a webinar covering the theme of Generative AI Applications for Administrative Professionals.
Here is the complete prompt I created to help us identify the four elements:
“I want you to act as an expert data science webinar moderator. You are an expert webinar moderator on artificial intelligence, administrative management, and career development topics. You are creating a webinar landing page on a webinar covering the theme of Generative AI Applications for Administrative Professionals. Follow my instructions thoroughly! Do not deviate from them. Provide a step-by-step reasoning of why you’re making the decisions you are making.
Create an engaging, professional title for the webinar. The primary audiences are Executive Assistants, administrative professionals, office managers, HR managers, and enthusiasts.
Write a 100- to 1050-word abstract for the webinar. The abstract should have two paragraphs; the first paragraph explains the importance of the webinar.
Provide 3 takeaways for the webinar for audiences to remember.
Have a credible, professional, and accessible voice and tone. A good example would be that of Harvard Business Review magazine articles and McKinsey reports.
Avoid bad copy.
Avoid factual errors.”
The instruction is the first sentence, asking the tool to act as a data science webinar moderator. After that, I include the context: “You are an expert webinar moderator on topics related to artificial intelligence, administrative management, and career development.”
After that, the following information is the question I want the GenAI tool to solve—input data, which is to create a webinar landing page for a webinar covering the theme of Generative AI Applications for Administrative Professionals.
Finally, I explained the format of the output I want—an output indicator—including a command to follow my instructions carefully and avoid mistakes or the use of incorrect information. Note that I also ask for a step-by-step description of how the tool is reasoning while creating the output. This helps me check if the “reasoning” is according to the logic of my input—as in, checking if the tool understands what I want as output.
(If you are curious about the output, please copy the prompt and test it with your preferred generative AI chatbot.)
I encourage you to read more about the different prompt engineering techniques or templates used to create effective questions or instructions for AI models, like ChatGPT, to get the desired responses.
Compare Different Tools
Experimentation and curiosity are crucial to understanding what outputs you can get. They also help you keep refining the content you want. Compare different tools and ask the same question to check what best fits your purpose. Comparing the two outputs, I note that ChatGPT lists “Experiment and Adjust,” an element that is crucial to me and that I want to share with you in this article. So, “Experiment and Adjust” is part of my “customized” five-tips list.

Making Prompt Engineering Your Superpower
Prompt engineering has become one of the most basic and in-demand skills everyone who uses generative AI technology should master to be effective at work, according to a Forbes article. Mastering this skill can help us stay ahead of the curve and expand our tech-savvy expertise. But if you really want to use GenAI tools effectively, you have to be skilled – you have to be a creative thinker, a creative problem-solver, an active learner. Here are four recommendations from a lifelong learner:
Join AI learning platforms
Attend webinars and conferences, enroll in online training, read articles, and create your learning networks. Doing so will make you a proactive learner and help you stay ahead of the game.
Practice every day
The best way to learn something new is to practice it daily. I started by testing tools to help me plan trips, create document titles and subtitles, generate images for posts and presentations, summarize texts, and create LinkedIn posts. Be creative and remember these tools can help in various ways.
Teach what you learn
Teaching enhances your accountability and helps build a learning environment. Reflect on what you have learned. As Seneca said, “While we teach, we learn.”
Exercise critical thinking
Take control of the content you create with the tool. Check for any false information or hallucinations (fabricated information presented as factual). Never share sensitive or personal information in your prompts. The output is a suggestion, so make the content yours. Keep your own voice and personal touch and refine the output through conversational interaction.
Call to Action
Now that you have learned the importance of understanding prompt engineering techniques, it’s time to put this knowledge into practice and plan to learn more about the topic. What will you do to improve your understanding and use of GenAI tools? Challenge yourself to integrate these tools into your daily tasks over the next week.
For example, check with colleagues about how they use ChatGPT or other tools, create a presentation, brainstorm projects, or develop market content for your personal brand. My first big step was enrolling in an online prompt engineering certification course. We will all use these tools for different tasks and purposes, so identify your current needs and challenge yourself. These small steps can significantly enhance your productivity and tech skills. Remember, continuous learning and experimenting with AI will keep you ahead of the curve and add immense value to your professional growth.
You are the pilot! Take your seat and navigate your journey to mastering AI skills and making it your superpower.
References
3 In-Demand, High-Income AI Skills You Need In 2024 (forbes.com)
Examples of Prompts | Prompt Engineering Guide (promptingguide.ai)













Insightful article! You’ve redefined prompt engineering in such simple terms. Thanks for the clarity, Julia!
Hi Gifty,
Thank you so much for the feedback. I am happy so see that my message is clear and right to the point. I hope it can keep you motivated to learn more. You are the pilot!
Warm regards,
Julia